Flowable怎么通过委托表达式获取到Micronaut的bean
flowable Unknown property used in expression: ${testListener}
众所周知在spring中工作流引擎activiti/flowable是可以通过委托表达式获取到spring bean的。但在micronaut中会报这个异常,因为activiti/flowable官方已经集成好了spring,而micronaut并没有人帮你集成过,获取不到容器里的bean是理所当然的。
由于micronaut是个新框架,网上翻了一圈都没找到对路的文章,以及在micronaut中怎么解决。
无奈之下自能自己出手了,翻了翻flowable的源码,找到跟spring集成部分的代码,理解了一下,模仿着写了一个针对micronaut的简单集成,打通flowable和micronaut容器,经过一番调试之后问题解决。
在给任务节点设置监听器,运行到这个节点时会出现这个异常flowable Unknown property used in expression: ${testListener},监听器的设置如下图所示,设置了委托表达式delegateExpression,本意是想获取一个bean作为监听器。
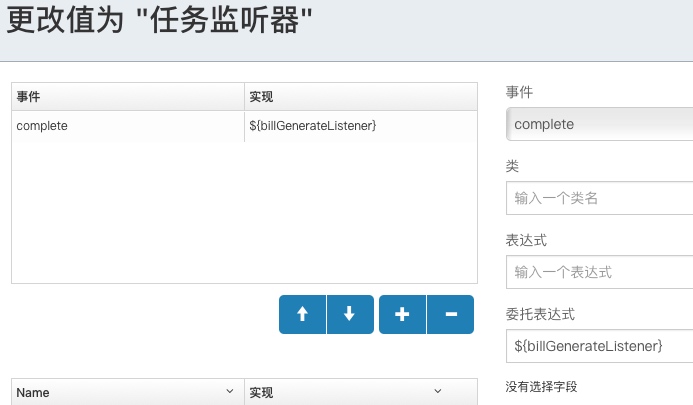
对应的xml为:
<userTask id="task1" name="task1" flowable:formFieldValidation="true">
<extensionElements>
<flowable:taskListener event="complete" delegateExpression="${billGenerateListener}">
</flowable:taskListener>
</extensionElements>
</userTask>
监听器代码如下:
@Context
@Named("billGenerateListener")//监听器名称,跟委托表达式里的设置对应
public class BillGenerateTaskListener implements TaskListener {
@Override
public void notify(final DelegateTask delegateTask) {
delegateTask.getTaskDefinitionKey();
final Map<String, Object> variables = delegateTask.getVariables();
final Object costPrice = variables.get("costPrice");
log.warn("Generate Bill...");
log.warn("costPrice:{}",costPrice);
}
}
下面直接看怎么解决的吧,不扯什么工作原理、底层机制,我们只是为了解决问题,直接抄了能用最好!
我们知道flowable引擎对象ProcessEngine一般是通过ProcessEngineConfiguration#buildProcessEngine()创建的,这是使用引擎的入口。
那么需要在ProcessEngineConfiguration中设置一个自己扩展的ProcessExpressionManager
cfg.setExpressionManager(
new MicronautExpressionManager(applicationContext, cfg.getBeans()));
MicronautExpressionManager:
public class MicronautExpressionManager extends ProcessExpressionManager {
protected ApplicationContext applicationContext;//micronaut的context
public MicronautExpressionManager(ApplicationContext applicationContext, Map<Object, Object> beans) {
super(beans);
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
protected ELResolver createElResolver(VariableContainer variableContainer) {
CompositeELResolver compositeElResolver = new CompositeELResolver();
compositeElResolver.add(createVariableElResolver(variableContainer));
compositeElResolver.add(createMicronautElResolver());//主要是这里
compositeElResolver.add(new ArrayELResolver());
compositeElResolver.add(new ListELResolver());
compositeElResolver.add(new MapELResolver());
compositeElResolver.add(new JsonNodeELResolver());
compositeElResolver.add(new BeanELResolver());
compositeElResolver.add(new CouldNotResolvePropertyELResolver());
return compositeElResolver;
}
protected ELResolver createMicronautElResolver() {
if (beans != null) {
return new ReadOnlyMapELResolver(beans);
} else {
// 还有这里,在表达式中暴露 application-context
return new MicronautApplicationContextElResolver(applicationContext);
}
}
}
再看下MicronautApplicationContextElResolver:
public class MicronautApplicationContextElResolver extends ELResolver {
protected ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public MicronautApplicationContextElResolver(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
//主要就是这里通过bean名称获取micronaut的bean
@Override
public Object getValue(ELContext context, Object base, Object property) {
if (base == null) {
String key = (String) property;
final Object o = applicationContext.getBean( Object.class, Qualifiers.byName(key));
if (o!=null) {
context.setPropertyResolved(true);
return o;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isReadOnly(ELContext context, Object base, Object property) {
return true;
}
@Override
public void setValue(ELContext context, Object base, Object property, Object value) {
if (base == null) {
String key = (String) property;
final Object o = applicationContext.getBean( Object.class, Qualifiers.byName(key));
if (o!=null) {
throw new FlowableException("Cannot set value of '" + property + "', it resolves to a bean defined in the micronaut application-context.");
}
}
}
@Override
public Class<?> getCommonPropertyType(ELContext context, Object arg) {
return Object.class;
}
@Override
public Iterator<FeatureDescriptor> getFeatureDescriptors(ELContext context, Object arg) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getType(ELContext context, Object arg1, Object arg2) {
return Object.class;
}
}
好了,抄完作业就阔以了。
原文发表于http://jenwang.me
更多交流请关注公众号:

本文永久链接: http://jenwang.me/15967788014795.html
进一步交流:
- Email:jenwang@foxmail.com
- 对于本博客某些话题感兴趣,希望进一步交流的,请加 qq 群:2825967
- 更多技术交流分享在圈子「架构杂谈」,跟老司机们聊聊互联网前沿技术、架构、工具、解决方案等